Applications in oil industries
Oil refining and PTA production
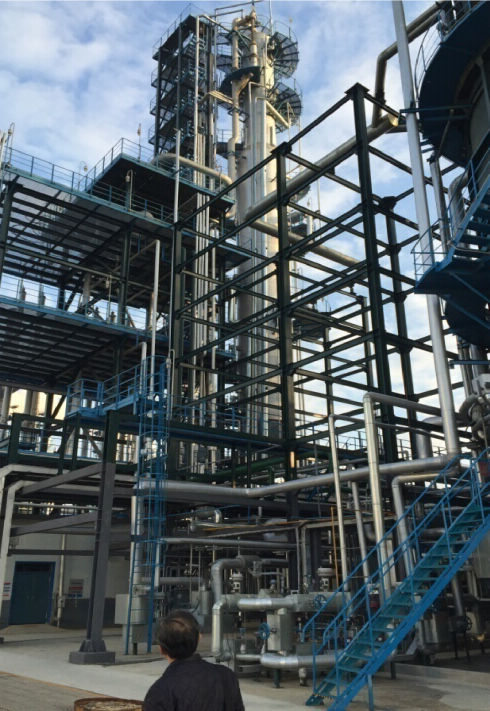

Atmospheric and vacuum distillation tower
Naphthenic acid corrosion
The acid value of crude oil is not directly linked to the naphthenic acid content because the chemical structure of naphthenic acid in different crude oils is often different, as a result they also come with different corrosivity. It is generally believed that when the acid value is greater than 0.5 mg · KOH / g, the crude oil can be very corrosive to most metals.
The corrosion of oil refining equipment caused by high acid value oil has now become a major concern of oil refineries. Among them, the high acid value crude oil represented by Russian, Middle East and Northern China oil has shown particularly high corrosive abilitity on tower internals such as column packing.
Terephthalic acid (PTA) manufacture
Solvent dehydration system towers
Acetic acid generally does not corrode the stainless steel packings. However, as the bromine ion concentration in the acetic acid solution increases, the corrosion rate of tower packings starts to accelerate.
During the production of PTA, bromide is added to tetrabromoethane according to the production process and is present in the material. When the concentration of acetic acid is increased to 85% -95%, it becomes more corrosive, and the temperature also plays a role in accelerating the corrosion.
As a negtive active ion, Bromine can stick on the surface of stainless steel and destroy the protective passive film, and forms pitting corrosions. Then Bromine ions are further concentrated in the pit, which results in deeper pitting corrosion.
Corrosion mechanism
How is 316L stainless steel corroded in refinery distillation towers?
Hydrogen sulfide is a weak inorganic acid and naphthenic acid is a weak organic acid, the reaction
of hydrogen sulfide with metal will produce a protective ferrous sulfide film, naphthenic acid
is different, and the product produced after reaction with metal is oil Soluble, can be taken away
by oil flow.
Naphthenic acid is not corrosive to metals at room temperature, but can react with iron and form
naphthenate at high temperature, this process causes severe corrosion.
The corrosion of naphthenic acid starts at 220 ℃, and the corrosion gradually increases with increasing temperature till 400 ℃
At 270 ~ 280 ℃: Corrosion first increases and then decreases after;
At 340 ~ 350 ℃: Corrosion continue increasing and reach the highest at 350 ℃;
At above 400 ℃: Corrosion not common, because the naphthenic acid in crude oil has been mostly
gasified.
The corroded stainless steel packing causes uneven liquid dispersion, which further deepens
the corrosion and reduces the gas-liquid exchange efficiency of the entire tower. In severe
cases, the stainless steel packing in the tower collapsed, and eventually the tower had to be
dismantled for maintenance, which significantly increased the maintenance time and resulted in
delayed production.
Ceramic foam packing
Also avaible
Fully acid proof
Built with our toughest Silicon Carbide
ceramic material, same as the wire gauze
packing.
Fast and even
liquid dispersion
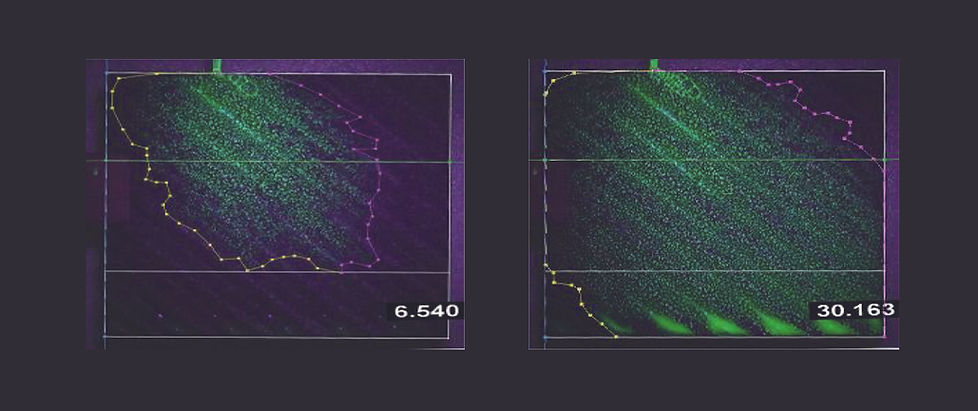
Better liquid dispersion ability than metal
packing. As shown in the test below, liquid
is uniformly distributed across the packing.
Extremely high
specific surface area
The ceramic foam packing is made with
our patented technology, which generates
interconnected 3D pore structure with
adjustable pore size and porosity. The
result is a very high specific surface area
and distallation efficiency.

Further reading
Steel packing spontaneous combustion
Many oil refineries are prone to natural packing due to improper maintenance.
Spontaneous combustion in most cases are caused by ferrous sulfide. During tower maintenance, as oil inside the tower is withdrawn, the FeS from internal corrosion gradually expose to air.
Typical cleaning process uses steam purge, which gasifies the oil film on the surface of FeS2, this leaves FeS2 in direct contact with O2.
As tower opens for maintenance, large amount of air enters the tower, the oxidation reaction continues and releases heat, which causes the oil and gas on the packing surface to exceed the ignition point of the residual oil and ultimately causes fire accidents.
Iron sulfide has a strong reducibility, and produce a strong redox reaction and emit a lot of heat upon coming into contact with oxygen in the air. The heat is enough to burn the low-boiling light flammable components in the residue. This is the spontaneous combustion of iron sulfide. Spontaneous
combustion (such as iron sulfide) will be deposited on the surface of the packing during the operation of the tower, and it is difficult for the traditional cleaning method to completely remove the spontaneous combustion. When the tower is shut down and encounters air, iron sulfide can spontaneously ignite at ambient temperature, resulting in a fire.
In some cases, the process of new packing installation may also have fire hazrds, as new packings has a layer of combustible lubricating oil film, sparks generated by welding, cutting, grinding and other operations above the packing can easily cause fire to the packing.
To prevent the ferrous sulfide from filling naturally during the shutdown, the vacume distillation tower should be cooled to ambient temperature, then purged with inert gas, and then cleaned to remove all residues. This ensures the ferrous sulfide is passivated to prevent fire.
Ceramic packing from Standard Ceramic completely eleminates the risk of spontaneous combustion by using chemically stable, non-flammable Silicon Carbide material, and with our revolutionary wire gauze design, we make sure the packing combines the high efficiency of tradtional metal wire gauze packing and the corrosion resistancy of the traditional ceramic packing.